Today, we’ll talk about your vehicle’s cooling system and how it works. Your vehicle’s cooling system consists of the water pump, radiator, cooling fans, and thermostat. We’ll talk about radiators and different types of radiators in this post.
What is The Radiator, and what does it do?
Radiators are heat exchangers that allow thermal energy to be transferred from one medium to another for cooling and heating.
A radiator is a cooling device with a wide cooling surface and a big volume of air that distributes through the water to efficiently cool it.
Radiators are used to cool the internal combustion engine in automobiles and have a wide range of uses in the automotive industry. They’re also utilised in piston-engined aeroplanes, railway locomotives, motorbikes, stationary generating plants, and other applications.
The direction of water flow through radiators is used to classify them. Some radiators have a top-to-bottom flow, whereas others have a top-to-bottom flow. In a cross flow type radiator, water flows horizontally from one input tank on one side to another tank on the other side.
Because of their great heat conductivity, copper and brass are commonly used in radiators. Soldering connects the various components of the radiators almost entirely.
Radiator Types
Radiators are divided into two categories.
- Tubular type
- Cellular type
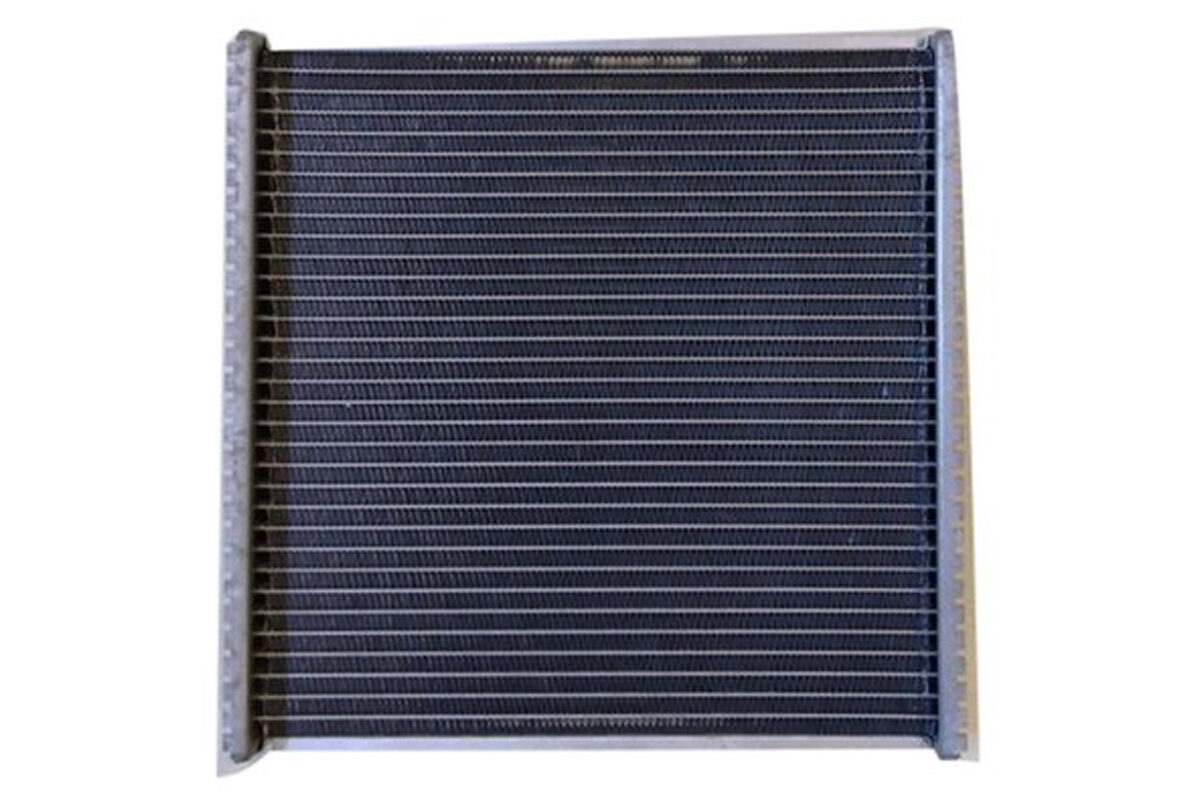
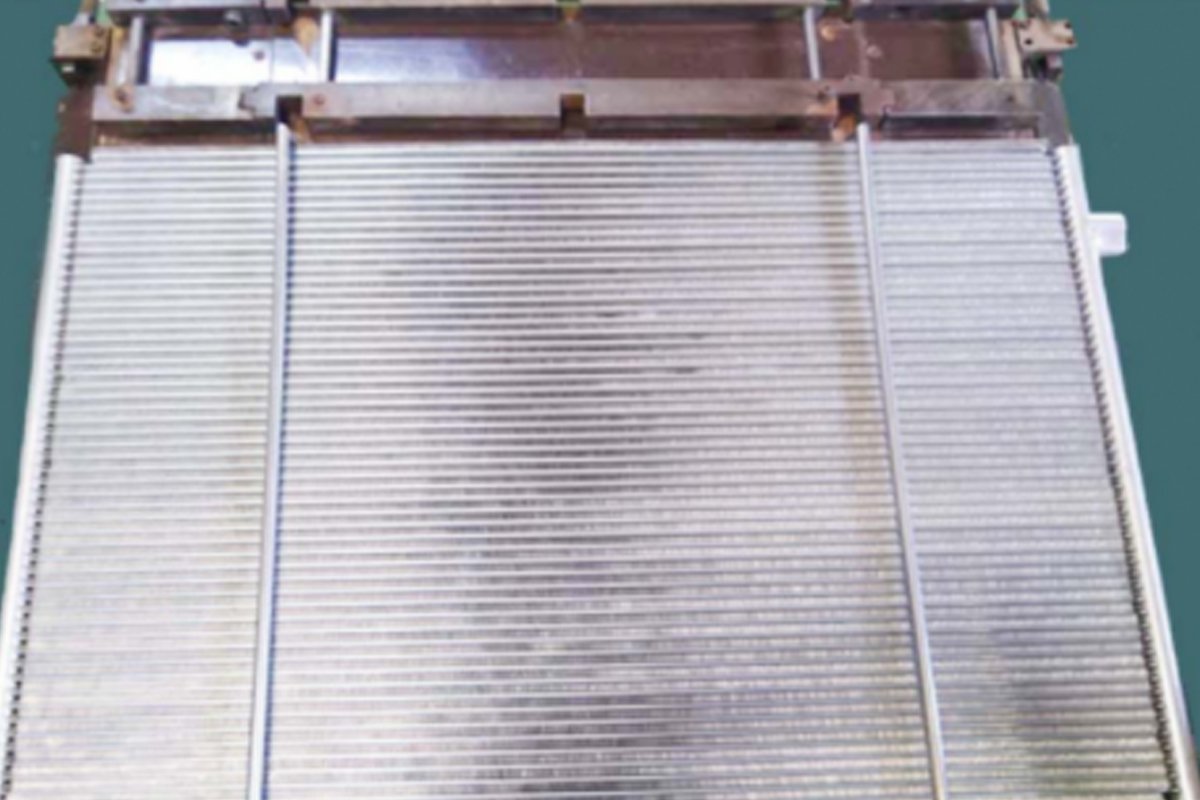
Core of Tubular Type
The top and lower tanks are connected by a network of tubes through which water travels in a tubular type core. To enhance heat transfer, fins are put around the tubes. As air travels around the exterior of the tubes and between the fins, it absorbs heat from the water.
Because water flows through all of the tubes of a tubular radiator, if one becomes blocked, the entire tube loses its cooling function. The blockage of any channel in a cellular radiator results in a loss of just a tiny portion of the overall cooling surface.
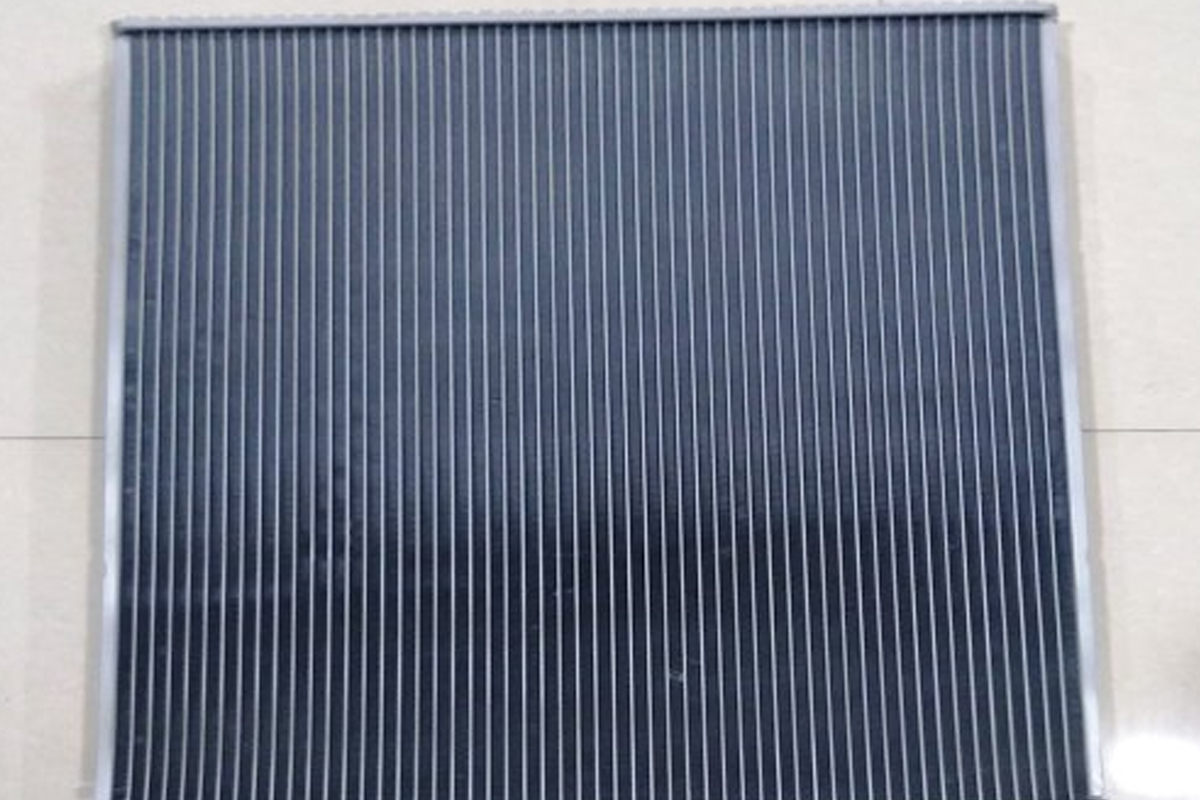
Core of Cellular Type
Air travels through the tubes and water flows through the gaps between them in a cellular type core.
The core is made up of a huge number of separate air cells that are encased in water. The cellular type is sometimes referred to as a honeycomb radiator because to its look, particularly when the cells in front are hexagonal in shape.
The blockage of any channel in a cellular radiator results in a loss of just a tiny portion of the overall cooling surface.
Is it Possible to Drive a Car Without a Radiator?
You can start your automobile without a radiator, but it’s a dangerous proposition. As long as the engine does not overheat, you will not do any damage. It’s not an issue if you don’t run it long enough for the engine to become too hot. If your automobile overheats, you must turn it off and allow it to cool down by convection.
Radiators are, in theory, entirely optional on an engine. Air-cooled engines have been around for quite some time. Cooling fins on these radiators remove heat and release it into the air.
But,
However, if your automobile was built with a radiator in mind, you’ll need one. There is no need to get rid of it.
What Makes an Engine Overheat?
An inadequate amount of water in the cooling system causes overheating. Clogged radiators and water passageways, belt slippage, demanding thermostat, late ignition timing, improper valve timing, pre-ignition, too tight bearing, low engine oil level, clogged exhaust system, and other factors can all contribute to this.
What Are the Symptoms of a Faulty Radiator?
- When the coolant can’t get to where it needs to go to cool the engine, it warms up.
- The hoses may be blocked, or the coolant level may be too low.
- A warning light may appear on the dashboard, or the temperature gauge may indicate that it is excessively hot.
- You may detect the scent of antifreeze or a tell-tale puddle on the garage floor if a hose is damaged or the radiator is rusted with rust.
- If you notice smoke coming from beneath the hood, it’s possible that coolant has leaked onto the engine and is being burned up.
- If you notice smoke escaping from the muffler, it’s possible that the head gasket has been damaged by the heated engine.